The landscape of real estate investment is diverse, but one sector that’s gaining attention, thanks to demographic shifts, is senior living. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or new to the field, understanding the nuances of investing in facilities for the elderly is crucial. Here, we’ve compiled an extensive FAQ to guide you through the complexities and opportunities in senior living investments.
What is Senior Living Investment?
Senior living investment involves channeling funds into properties or businesses dedicated to providing housing and care for the elderly. This can range from independent living for active seniors to memory care for those with dementia.
Why Invest in Senior Living?
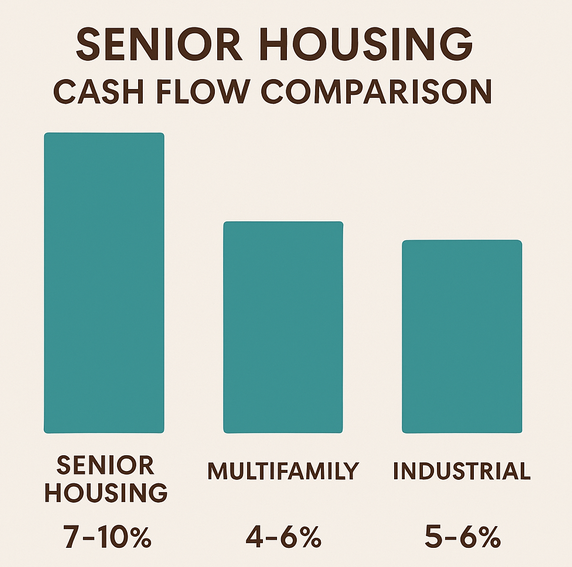
The aging population, especially the baby boomers retiring, creates a robust demand for senior housing. This sector offers potential for stable income due to long-term occupancy, capital appreciation, and its essential nature, making it relatively resilient to economic downturns.
Types of Senior Living Facilities
Investments can be made in:
- Independent Living: For self-sufficient seniors.
- Assisted Living: Offering help with daily activities.
- Memory Care: Tailored for individuals with memory issues.
- Continuing Care Retirement Communities (CCRCs): Providing a spectrum of care as needs evolve.
- Skilled Nursing Facilities (SNFs): For medical and rehabilitative care.
Starting Your Investment Journey
Begin with thorough research, financial analysis, and perhaps by partnering with seasoned operators or through investment vehicles like REITs. Consulting with industry experts can also pave the way for informed decisions.
Risks Involved
Investments here aren’t without risks, including regulatory changes, market saturation, operational complexity, and economic fluctuations. Understanding these can help mitigate potential downsides.
Accredited Investor Status
Many opportunities in senior living are restricted to accredited investors due to SEC regulations. This status is determined by your financial thresholds, ensuring investors have the capacity to bear the risk of loss.
Passive vs. Active Investment
Passive investing allows you to invest without managing day-to-day operations, often through funds or syndications where professionals handle the work.
What to Look for in an Investment
Location, management quality, financial health, regulatory compliance, and growth potential are key factors. A prime location with a demographic that supports demand is crucial.
Technology’s Role
Technology is revolutionizing senior living with telehealth, smart homes, and operational efficiencies, potentially boosting ROI and enhancing resident life quality.
Tax Implications
Investments might benefit from tax strategies like depreciation, interest deductions, or 1031 exchanges for tax deferral, but professional tax advice is recommended.
Performance Evaluation
Key metrics include occupancy rates, revenue per available room, net operating income, and resident satisfaction. Long-term market trends should also be considered.
Investment Beyond Accreditation
While many opportunities require accreditation, there are avenues for non-accredited investors, like public REITs or certain crowdfunding platforms, albeit with different risk profiles.
Lease Structures and Care Levels
Understanding lease types and how the care level affects both revenue and costs is vital. Higher care levels can mean higher income but at the expense of increased operational costs.
Government Funding Impact
Government programs like Medicaid can be pivotal for certain facilities. Policy changes can significantly sway profitability.
Selling and Transition
When selling, managing the transition for residents is as important as the financial deal to preserve the property’s value and reputation.
Maintenance and CapEx
Senior living facilities require ongoing maintenance and significant capital for upgrades, affecting long-term investment returns.
Insurance and Staffing
Insurance costs can be high due to the inherent risks, while staffing challenges directly impact operations and care quality.
Design Trends and Ethics
Modern facilities lean towards home-like settings, tech integration, and sometimes intergenerational activities. Ethical considerations might include sustainability or social impact goals.
Exit Strategies
Planning your exit, whether through sale, merger, or tax strategies like 1031 exchanges, should align with your investment timeline and market dynamics.
Healthcare Policy Changes
Staying informed about healthcare policy is crucial as it can affect funding, regulations, and operational costs.
Conclusion
Investing in senior living is not just about financial returns but also about making a difference in the quality of life for many. By understanding these FAQs, you can navigate this sector with more confidence, aligning your investment with both your financial goals and ethical standards. Whether you’re looking for passive income or active involvement, the senior living market offers unique opportunities for those willing to dive deep into its complexities.